Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 2, 2024.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
DKA is a life-threatening condition caused by dangerously high blood sugar levels. Your blood sugar levels become high because your body does not have enough insulin. Insulin helps move sugar out of the blood so it can be used for energy. The lack of insulin forces your body to use fat instead of sugar for energy. As fats are broken down, they leave chemicals called ketones that build up in your blood. Ketones are dangerous at high levels.
What increases my risk for DKA?
- Not enough insulin
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Infection or other illness
- Heart attack, stroke, trauma, or surgery
- Certain medicines such as steroids or blood pressure medicines
- Illegal drugs such as cocaine
- Emotional stress
- Pregnancy
What are the signs and symptoms of DKA?
- More thirst and more frequent urination than usual
- Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
- Blurry vision
- Dry mouth, eyes, and skin, or your face is red and warm
- Fast, deep breathing, and a faster heartbeat than normal for you
- Weak, tired, and confused
- Fruity, sweet breath
- Mood changes and irritability
How is DKA treated?
DKA can be life-threatening. You must get immediate medical attention. The goal of treatment is to replace lost body fluids, and to bring your blood sugar level back to normal.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I help prevent DKA?
The best way to prevent DKA is to control your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider for more information on how to manage your diabetes. The following may help decrease your risk for DKA:
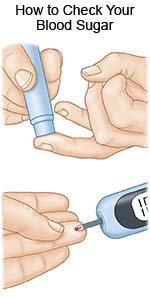
- Monitor your blood sugar levels closely. You levels may go up if you have an infection, are stressed, sick, or have a trauma. Check your blood sugar levels often. You may need to check at least 3 times each day. If your blood sugar level is too high, give yourself insulin as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Manage your sick days. When you are sick, you may not eat as much as you normally would. You may need to change the amount of insulin you give yourself. You may need to check your blood sugar level more often than usual. Make a plan with your healthcare provider about how to manage your diabetes when you are sick.
- Check your ketones as directed. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions about when you should check your blood or urine for ketones. Your healthcare provider may give you a machine to check your blood ketones. Urine ketones can be checked with sticks you dip in your urine. Do not exercise if you have ketones in your urine or blood. Exercise may increase the level of ketones in your blood or urine and cause dehydration.
- Know how to treat DKA. If you have signs of DKA, drink more liquids that do not contain sugar, such as water. Take your insulin as directed by your healthcare provider and go to the nearest emergency room.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You have a seizure.
- You begin to breathe fast, or are short of breath.
- You become weak and confused.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are more drowsy than usual.
When should I call my diabetes care team provider?
- You have fruity, sweet breath.
- You have severe, new stomach pain and are vomiting.
- Your blood sugar level is lower or higher than your healthcare provider says it should be.
- You have ketones in your blood or urine.
- You have a fever or chills.
- You are more thirsty than usual.
- You are urinating more often than usual.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Treatment options
- Medications for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Medications for Diabetic Ketoacidosis, in DM Type I
- Medications for Diabetic Ketoacidosis, in DM Type II
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
